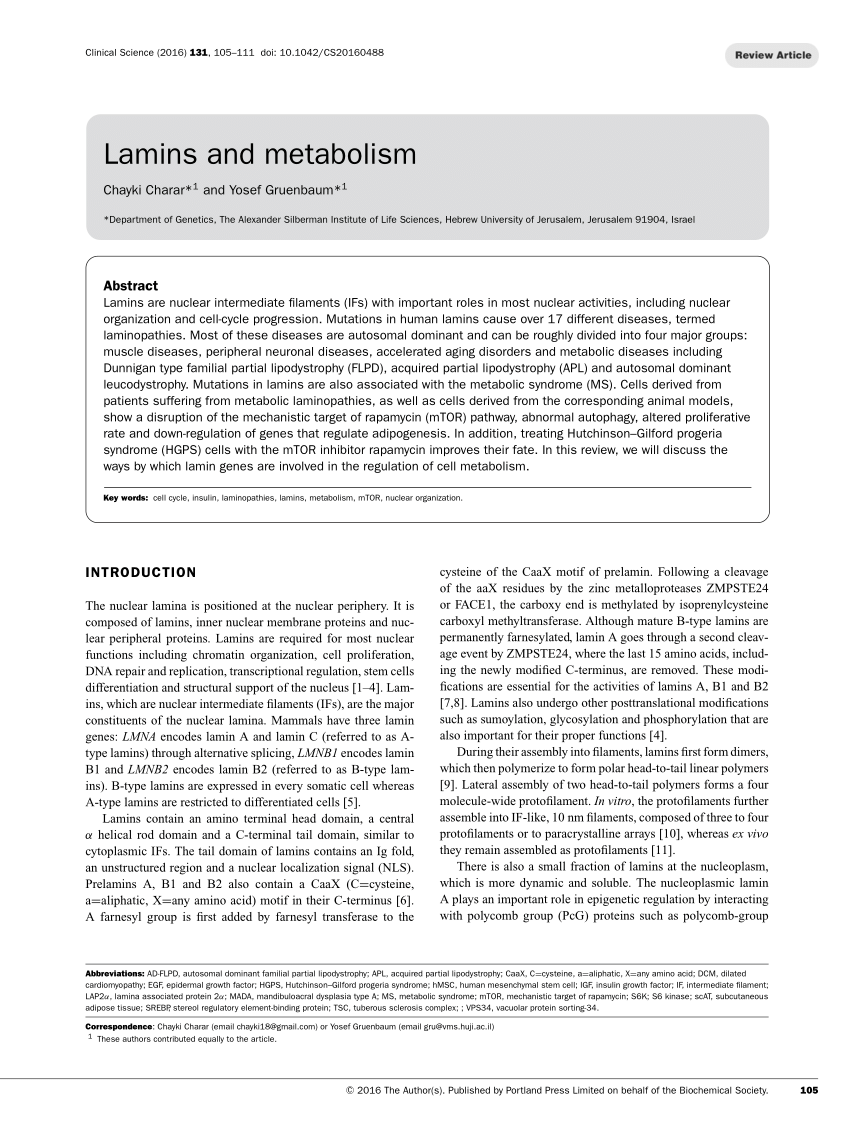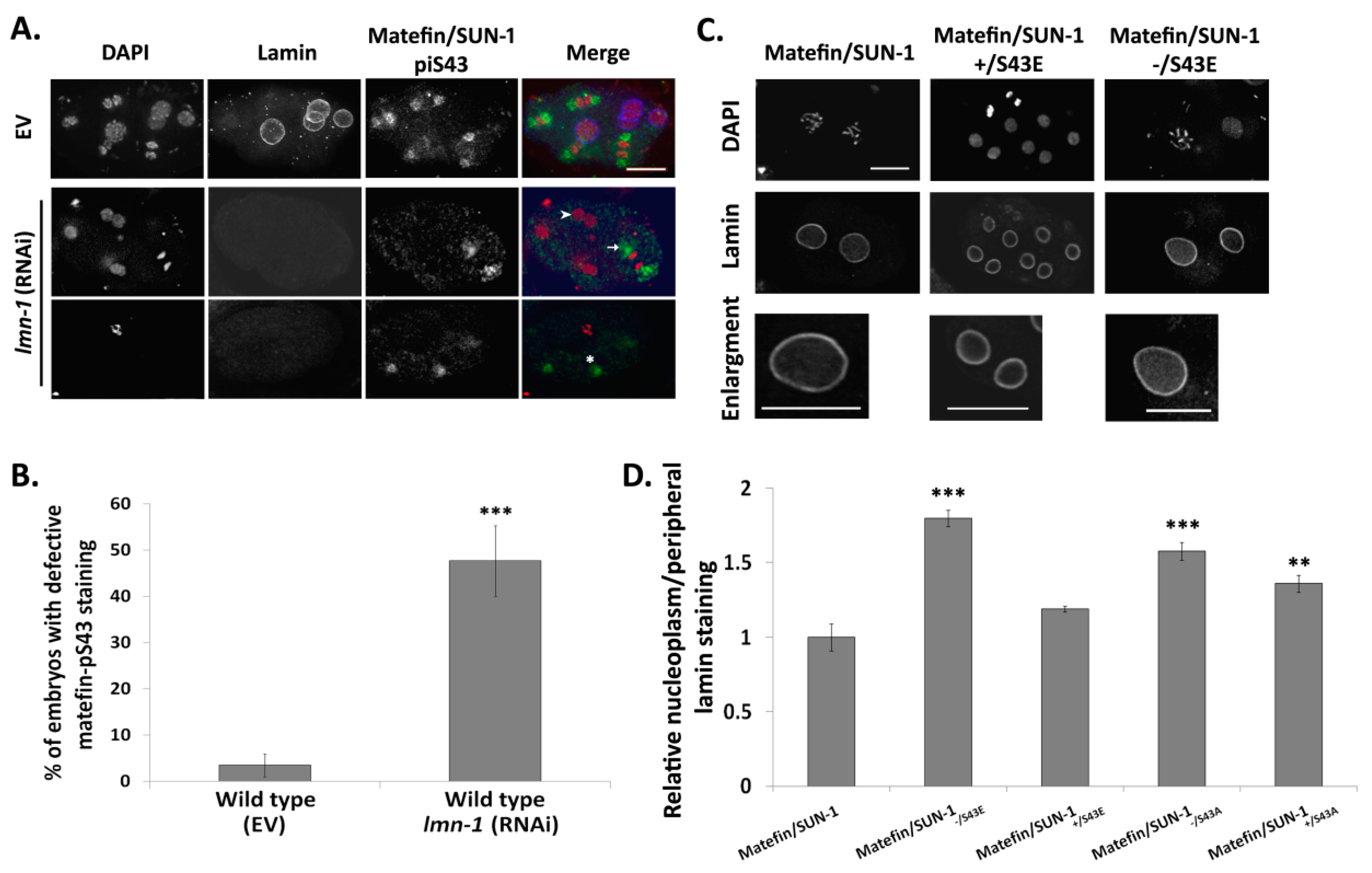
Cells | Free Full-Text | Matefin/SUN-1 Phosphorylation on Serine 43 Is Mediated by CDK-1 and Required for Its Localization to Centrosomes and Normal Mitosis in C. elegans Embryos | HTML

Yosef Gruenbaum's research works | Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem (HUJI) and other places

C. elegans Nuclear Envelope Proteins Emerin, MAN1, Lamin, and Nucleoporins Reveal Unique Timing of Nuclear Envelope Breakdown during Mitosis | Molecular Biology of the Cell
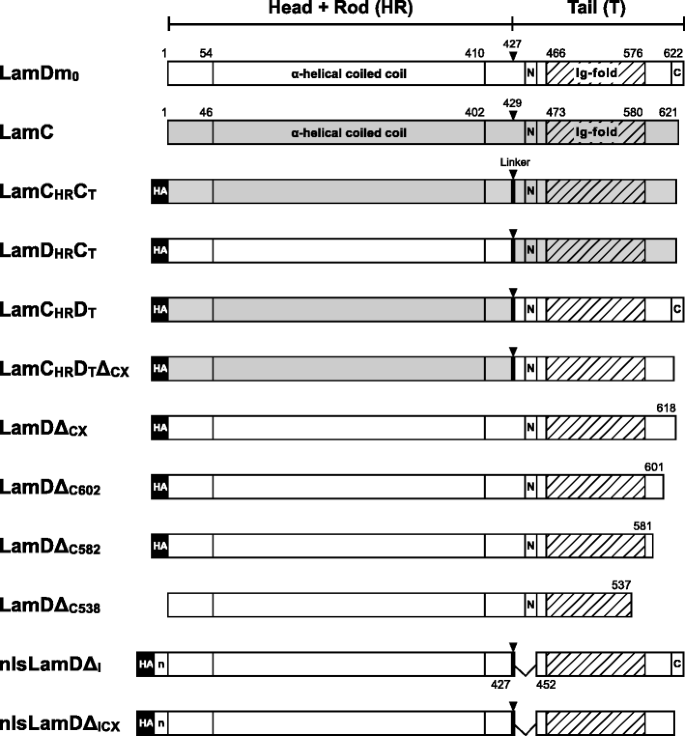
Non-farnesylated B-type lamin can tether chromatin inside the nucleus and its chromatin interaction requires the Ig-fold region | SpringerLink

PDF) Lamin-dependent Localization of UNC-84, A Protein Required for Nuclear Migration in Caenorhabditis elegans